Ethnic Representation in New Russell 3000 Director Appointments Has Fallen 22% Since 2022
Summary
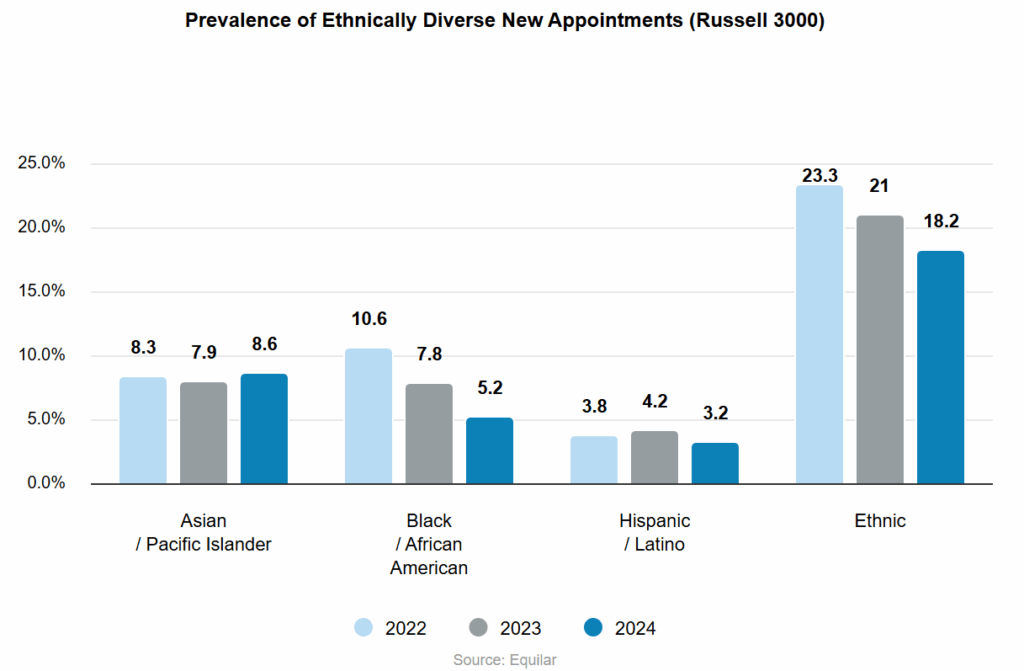
New data from Equilar on Russell 3000 board appointments shows a marked drop in ethnic diversity among newly appointed directors. The share of ethnically diverse individuals taking new board seats fell from 23.3% in 2022 to 18.2% in 2024 — a 21.9% decrease. Declines are concentrated among Black/African American and Hispanic/Latino appointees, while Asian/Pacific Islander new appointments rose modestly.
Key Points
- The prevalence of ethnically diverse new board appointees fell from 23.3% (2022) to 18.2% (2024), a 21.9% drop.
- New Black/African American director appointments fell 33.3% from 2023 to 2024 and are down more than 50% versus 2022.
- Hispanic/Latino new appointments dropped 23.8% from 2023 to 2024.
- New Asian/Pacific Islander appointments rose 8.9% in 2024, but overall Asian representation slipped slightly year‑over‑year.
- Overall ethnic representation across Russell 3000 boards rose 13.7% from 2022 to 2024, yet showed a 0.5% decline from 2023 to 2024, signalling a slowdown.
- By end‑2024 shares: Black/African American 7.9%, Asian/Pacific Islander 6.7%, Hispanic/Latino 3.6%.
- Sector differences are notable: technology (23.8%), utilities (23.3%) and consumer defensive (22.5%) lead; energy lags at 14.8%. Utilities has the highest share of Black/African American directors (12.2%).
Content Summary
Equilar’s analysis, summarised by Joyce Chen, links recent political and regulatory shifts — including the US federal executive order curtailing DEI programmes — with corporate behaviour: many public companies, particularly larger ones, appear to be reassessing or scaling back diversity efforts. The immediate effect is fewer ethnically diverse hires onto boards, concentrated among Black/African American and Hispanic/Latino candidates. Although aggregate representation has increased since 2022, the pace of progress slowed in 2024.
The dataset highlights both cross‑sector variation and the uneven nature of gains: some groups and sectors continue to make small strides while others see backsliding. The report suggests these trends could shape board composition and corporate governance discussions in the near term.
Context and Relevance
Why this matters: board diversity is tied to governance quality, risk oversight and investor expectations. A retreat or slowdown in appointments of ethnically diverse directors could have consequences for decision‑making, stakeholder relations and regulatory scrutiny. The finding is timely given heightened political attention on DEI, and it dovetails with investor stewardship agendas that increasingly weigh diversity metrics when assessing boards.
For governance professionals, investors and diversity advocates, the data flags where progress is faltering and which sectors might warrant closer engagement or targeted pipeline work.
Why should I read this?
Short version: if you care about board quality, investor risk or who’s sitting round the boardroom table, this is worth five minutes. The piece pulls out crisp numbers showing a real slowdown in hiring ethnically diverse directors — not just noise. It’s a clear signal that political shifts are filtering down to corporate appointments, and that some groups are being hit harder than others.